How AI can Improve Businesses in the coming Years?
 The stereotype that AI is only found in science-fiction dystopias is fading as AI advances and becomes more pervasive in our daily lives. A household presence (hi, Alexa!) and a household name (artificial intelligence) are now both commonplace.
The stereotype that AI is only found in science-fiction dystopias is fading as AI advances and becomes more pervasive in our daily lives. A household presence (hi, Alexa!) and a household name (artificial intelligence) are now both commonplace.
Although the acceptance of AI in modern society is a recent phenomenon, the idea is not. Although the modern field of artificial intelligence (AI) was founded in 1956, significant advancements toward creating an AI system and making it a technological reality required decades of work.
Artificial intelligence is used in business in a variety of ways. In reality, most of us deal with AI daily in one way or another. Artificial intelligence is already upending practically every business process in every industry, from the routine to the breathtaking. To maintain a competitive edge, AI technologies are becoming more and more necessary.
What is AI?
It’s crucial to define AI technologies before examining how they are affecting the business world. Any type of computer software that performs actions akin to those performed by a human, such as planning, learning, and problem-solving, is referred to as “artificial intelligence” in the broadest sense. Specific applications are not covered by the term “artificial intelligence,” which is technically correct but leaves out important details. We need to look further to determine the type of AI that is most common in business.
Machine Learning: One of the most popular categories of artificial intelligence (AI) being developed for commercial use right now is machine learning. The main purpose of machine learning is to quickly process large amounts of data. Artificial intelligence (AIs) use algorithms that seem to “learn” over time.
A machine-learning algorithm’s modelling ought to advance as more data are fed into it. Large data sets that are increasingly being captured by connected devices and the Internet of Things can be usefully contextualized for humans using machine learning.
If you are in charge of a manufacturing facility, your equipment is probably connected to the network. An ongoing stream of data about functionality, production, and other topics is fed to a central location by connected devices. Unfortunately, there is simply too much data to ever sort through, and even if there were, most of the patterns would probably be missed.
Rapid data analysis using machine learning can spot patterns and anomalies in the data as it is being gathered. A machine-learning algorithm can detect when a machine in a manufacturing facility is operating at a reduced capacity and alert decision-makers that a preventive maintenance team needs to be sent out.
However, the field of machine learning is also quite broad. Deep learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that was made possible by the development of artificial neural networks, which are networks of connected artificial intelligence “nodes”.
Deep Understanding: Deep learning, a more focused variation of machine learning, uses neural networks to engage in nonlinear reasoning. Deep learning is necessary to carry out more sophisticated tasks, like fraud detection. It can do this by simultaneously analyzing a variety of factors.
For instance, numerous factors must be recognized, examined, and addressed at once for self-driving cars to function. Self-driving cars can contextualize information from their sensors, such as the distance to other objects, their speed, and a forecast of where they will be in the next five to ten seconds, with the aid of deep learning algorithms. A self-driving car can use this data to make decisions like when to change lanes by quickly calculating all this information.
Deep learning holds great promise for the business world and will probably be applied more frequently. As more data is collected, deep-learning models continue to perform better than older machine-learning algorithms, which tend to plateau once a certain amount of data has been collected. Deep learning models are now much more scalable, detailed, and independent as a result.
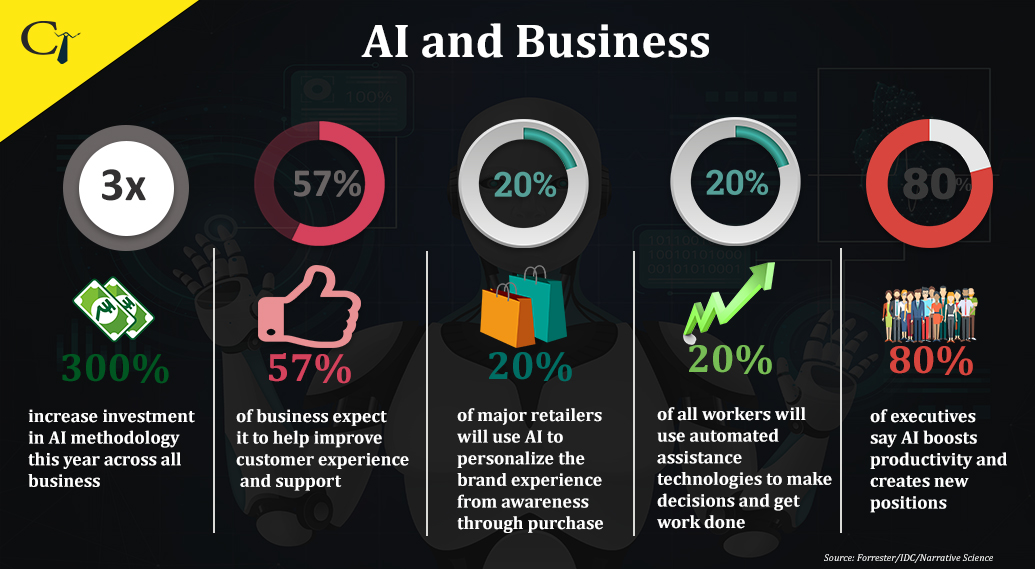
Modern Business and AI:
Artificial intelligence is typically considered to be a supporting tool rather than a replacement for human intelligence and ingenuity. AI is adept at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data much more quickly than a human brain could, even though it currently struggles to complete commonsense tasks in the real world. The synthesized courses of action can then be presented to the human user by artificial intelligence software. In this way, we can use AI to speed up the decision-making process and game out the potential outcomes of each action.
Amir Husain, founder and CEO of machine-learning company SparkCognition, said that artificial intelligence is somewhat the second coming of software. It’s a type of software that can act even in circumstances that the programmers hadn’t anticipated. Compared to conventional software, artificial intelligence has a wider range of decision-making options. “.
These characteristics make AI extremely valuable across a wide range of industries, whether it’s just assisting staff and visitors in efficiently navigating a corporate campus or handling a task as complex as monitoring a wind turbine to foretell when it will require repairs.
Conclusion:
~ Businesses use artificial intelligence for a variety of purposes, including data aggregation and job process streamlining.
~ When it comes to blue-collar jobs in particular, researchers are unsure of what artificial intelligence will mean for the future of business.
~ AI is anticipated to bring digital technology out of the two-dimensional screen and into the three-dimensional real world that surrounds a person.
~ The goal of this article is to educate business owners and employees about how artificial intelligence is changing the commercial world.
Related Posts
Instagram Implements Advanced Protections for Teen Users.

5 Skills to Become a Successful Social Media Marketer

LinkedIn Adds AI Training Opt-out Option

What Video Editing Software Do Youtubers Use in 2024?

How VoIP Services are changing the Way We Make Calls






































